I have a 2TB WD Re hard drive that I was planning to use in a RAID 1 configuration for data storage on my desktop, but I am unable to delete the existing partitions and reformat the drive. The HDD was previously used in another system, but has been inactive for a while and I don’t remember the details of its previous usage. Based on the name and the fact that Windows is showing double its extra capacity, it was likely used to store backups and possibly as part of a Storage Spaces drive.
I am running Windows 10 Pro 1909 and when I view the drive in Disk Manager, it shows the following: 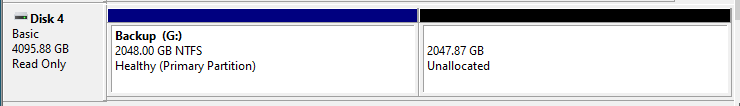
I have tried using DiskPart to clear the read-only attribute from the drive. Each time I run the command, DiskPart tells me it was successful in clearing the attribute, but the disk remains read-only. I have also attempted to use EaseUS Tools M and EaseUS Partition Master Professional to no avail.
I have read on other websites that it may be possible to clear the read-only attribute by editing the registry at the following location: Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\StorageDevicePolicies.
However, I do not have this path in my registry and have not been able to find a similar setting.
I have also tried running CHKDSK on the drive, but am unable to run it in /F mode due to the read-only setting. When I run CHKDSK in read-only mode, it returns no issues.
I am running out of ideas on how to fix this issue. The only other suggestions I have come across are to try using GParted in Linux or to overwrite the disk with dd in Linux. I do not have Linux installed on any physical computers (only VMs), but I am willing to set up a Linux system if necessary. If all else fails, I do have a hammer that I can use as a last resort.
If you have any additional ideas on things to try, I would welcome them.
3 Answers
Introduction
Windows 10 is a widely used operating system that offers several features for managing hard drives. However, there are times when users encounter issues that prevent them from performing certain tasks. One such problem is the inability to remove the read-only attribute from a hard drive. This issue can be frustrating, especially when you need to format the drive or create new partitions. In this blog post, we will discuss the possible reasons why Windows 10 is unable to remove the read-only attribute from a hard drive and explore some solutions to fix the issue.
Possible Reasons for the Issue
Before we dive into the solutions, let’s first understand the possible reasons why Windows 10 is unable to remove the read-only attribute from a hard drive.
One reason could be that the hard drive is write-protected, which means that you cannot modify or delete the data on the drive. This could be due to physical damage to the drive or a software issue that has caused the write-protection setting to be enabled.
Another reason could be that the read-only attribute has been set on the hard drive, which means that you can read the data on the drive, but you cannot modify or delete it. This setting could have been enabled by the user or by a software program.
Lastly, the issue could be related to the file system on the hard drive. If the file system is corrupted or damaged, it can prevent you from modifying or deleting the data on the drive.
Solutions to Fix the Issue
Now that we have a better understanding of the possible reasons for the issue, let’s explore some solutions to fix the read-only attribute problem in Windows 10.
Solution 1: Clear Read-only Attribute Using DiskPart
DiskPart is a command-line tool that can be used to manage hard drives in Windows. Here’s how you can use DiskPart to clear the read-only attribute from a hard drive:
1. Open the Command Prompt as an administrator.
2. Type “diskpart” and press Enter.
3. Type “list disk” and press Enter. This will display a list of all the hard drives connected to your computer.
4. Identify the disk that you want to clear the read-only attribute from and type “select disk x” (replace “x” with the disk number) and press Enter.
5. Type “attributes disk clear readonly” and press Enter.
6. Exit DiskPart by typing “exit” and pressing Enter.
After completing these steps, check if the read-only attribute has been cleared from the hard drive.
Solution 2: Format the Hard Drive
If the read-only attribute cannot be cleared using DiskPart, you may need to format the hard drive. However, keep in mind that formatting the drive will erase all the data on it. Here’s how you can format the hard drive:
1. Open Disk Management by right-clicking on the Start menu and selecting “Disk Management”.
2. Locate the hard drive that you want to format and right-click on it.
3. Select “Format” and configure the settings according to your preferences.
4. Click on “OK” to begin the formatting process.
Once the formatting process is complete, check if the read-only attribute has been removed from the hard drive.
Solution 3: Use a Linux Live CD
If the above solutions do not work, you can try using a Linux Live CD to access the hard drive. Here’s how you can do it:
1. Download a Linux Live CD such as Ubuntu or Linux Mint.
2. Burn the ISO file to a CD or USB drive.
3. Boot your computer from the CD or USB drive.
4. Once you have booted into the Linux environment, open the file manager and locate the hard drive.
5. Right-click on the hard drive and select “Properties”.
6. Navigate to the “Permissions” tab and ensure that you have write access to the drive.
7. Try modifying or deleting the data on the hard drive.
Using a Linux Live CD can help you bypass any limitations imposed by Windows and enable you to modify the data on the hard drive.
Solution 4: Use Third-party Software
If none of the above solutions work, you can try using third-party software such as EaseUS Partition Master or MiniTool Partition Wizard. These tools offer advanced features for managing hard drives and can help you clear the read-only attribute from a hard drive. However, keep in mind that these tools may not be free and may require a license to use.
Solution 5: Seek Professional Help
If all else fails, you may need to seek professional help from a data recovery specialist or a computer technician. They can examine the hard drive and determine the root cause of the read-only attribute problem. They may also be able to recover any data that was lost during the process.
Conclusion
The read-only attribute problem in Windows 10 can prevent you from modifying or deleting the data on a hard drive. However, by following the solutions discussed in this blog post, you can fix the issue and regain access to your data. Remember to always back up your data before attempting any modifications to your hard drive to prevent any data loss.
I understand that you are unable to delete the existing partitions or reformat your hard drive due to it being read-only. Here are a few things you can try to fix this issue:
- Check if the hard drive is connected properly: Make sure the hard drive is connected firmly to the motherboard or the external enclosure. If you are using an external hard drive, try connecting it to a different USB port or to a different computer to check if the issue persists.
- Check for any hardware issues: If you suspect that the hard drive may be faulty, you can try testing it using a hardware diagnostic tool. You can also try connecting the hard drive to a different motherboard or external enclosure to see if it works.
- Disconnect other hard drives: If you have multiple hard drives connected to your computer, try disconnecting all of them except the hard drive that you want to format. This will ensure that there are no conflicts between the hard drives that may be causing the issue.
- Run DiskPart in Safe Mode: Try booting your computer into Safe Mode and running DiskPart to clear the read-only attribute. To do this, follow these steps:
- Restart your computer and press the F8 key repeatedly until the “Advanced Boot Options” screen appears.
- Select “Safe Mode” and press Enter.
- Once the system has booted into Safe Mode, open a command prompt as an administrator and type the following commands:
diskpart
list disk
select disk X (replace X with the number of the hard drive that you want to format)
attributes disk clear readonly
exit- Edit the registry: If the above steps don’t work, you can try editing the registry to clear the read-only attribute. To do this, follow these steps:
- Press the Windows key + R to open the “Run” dialog box.
- Type “regedit” and press Enter to open the Registry Editor.
- Navigate to the following key: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\StorageDevicePolicies
- If the “StorageDevicePolicies” key doesn’t exist, right-click on the “Control” key and select “New > Key.” Name the new key “StorageDevicePolicies.”
- Right-click on the “StorageDevicePolicies” key and select “New > DWORD (32-bit) Value.”
- Name the new value “WriteProtect” and set its value to “0” (zero).
- Close the Registry Editor and restart your computer.
- Use GParted in Linux: If you are comfortable with using Linux, you can try booting a Linux Live USB and using the GParted partition editor to delete the existing partitions and reformat the hard drive.
I hope these suggestions help. Let me know if you have any questions or if you need further assistance.
Thanks for the insight, it helped me think through where the drive could have become locked. After reading your comment, I did some more research on the history of the drive. I started up the Windows Server 2012R2 machine it was previously used with and connected the drive. I discovered that it was used as a rotating backup drive for a Windows Server 2012 R2 Essentials machine, and it was thinly provisioned for double its capacity using Storage Spaces.
I’m not sure if the drive became locked due to its use as a backup drive or because of Storage Spaces (I’m leaning towards the backup drive, based on the fact that the backup wizard formats and configures the drive, according to Microsoft’s server backup documentation). Regardless of the cause, the drive was indeed locked. I was able to use the domain admin account to unlock the drive and clear the configuration from the old machine.