When I operate my hackintosh (although it’s not directly related), the RAM on my computer is frequently compressed. As a result, it runs much faster than it does on Windows 10. In fact, very little memory is being compressed, and when I attempt to reopen an application, the paging process is quite sluggish.
2 Answers
Introduction
RAM compression is a process used by the operating system to free up memory space by compressing the data stored in memory. This helps to reduce the amount of memory used by the system, making it more efficient. However, in some cases, Windows 10 may not compress memory frequently enough, leading to slow performance and other issues. In this blog post, we will explore how you can force Windows 10 to compress memory more frequently.
What is RAM Compression?
RAM compression is a feature that is used to compress data stored in memory when the system is running low on memory. This helps to free up memory space and improve system performance. When the system needs to access the compressed data, it is decompressed and made available to the system. RAM compression is an effective way to improve system performance, especially on systems with limited memory.
Why is RAM Compression Important?
RAM compression is important because it helps to improve system performance by freeing up memory space. This is especially important on systems with limited memory, where the system may run out of memory and start using the hard drive as virtual memory. When the system starts using virtual memory, it can slow down significantly, leading to poor performance and other issues.
How to Force Windows 10 to Compress Memory More Frequently
There are several ways to force Windows 10 to compress memory more frequently. Here are some of the methods you can try:
Method 1: Increase the Memory Compression Threshold
One way to force Windows 10 to compress memory more frequently is to increase the memory compression threshold. The memory compression threshold determines how much memory must be free before the system starts compressing memory. By increasing the threshold, you can force the system to compress memory more frequently.
To increase the memory compression threshold, follow these steps:
1. Press the Windows key + R to open the Run dialog box.
2. Type regedit and press Enter to open the Registry Editor.
3. Navigate to the following key: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlSession ManagerMemory Management
4. Locate the CompressMemory registry value and double-click it.
5. Change the value data to 1.
6. Click OK and close the Registry Editor.
Method 2: Use a Third-Party Tool
Another way to force Windows 10 to compress memory more frequently is to use a third-party tool. There are several tools available that can help you optimize your system’s memory usage and improve performance. One such tool is Process Lasso.
Process Lasso is a powerful tool that allows you to prioritize and manage running processes on your system. It includes a memory compression feature that can help you free up memory space and improve system performance. To use Process Lasso to compress memory, follow these steps:
1. Download and install Process Lasso.
2. Open Process Lasso and click the Options button.
3. Click on the Memory tab.
4. Check the box next to “Enable memory compression”.
5. Set the compression threshold to your desired value.
6. Click OK to save your changes.
Method 3: Disable SuperFetch
SuperFetch is a feature in Windows 10 that is designed to improve system performance by preloading frequently used applications into memory. However, SuperFetch can sometimes use up a lot of memory, leading to slow performance and other issues. Disabling SuperFetch can help to free up memory space and improve system performance.
To disable SuperFetch, follow these steps:
1. Press the Windows key + R to open the Run dialog box.
2. Type services.msc and press Enter to open the Services window.
3. Locate the SuperFetch service and double-click it.
4. Set the Startup type to Disabled.
5. Click OK and close the Services window.
Method 4: Use ReadyBoost
ReadyBoost is a feature in Windows 10 that allows you to use a USB drive or SD card as additional memory. This can help to free up memory space and improve system performance. To use ReadyBoost, follow these steps:
1. Insert a USB drive or SD card into your computer.
2. Open File Explorer and right-click on the drive.
3. Select Properties from the context menu.
4. Click on the ReadyBoost tab.
5. Check the box next to “Use this device”.
6. Use the slider to set the amount of memory you want to use for ReadyBoost.
7. Click OK to save your changes.
Method 5: Disable Memory Compression
If none of the above methods work, you can try disabling memory compression altogether. This will free up memory space, but it may also lead to slower performance and other issues.
To disable memory compression, follow these steps:
1. Press the Windows key + R to open the Run dialog box.
2. Type regedit and press Enter to open the Registry Editor.
3. Navigate to the following key: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlSession ManagerMemory Management
4. Locate the CompressMemory registry value and double-click it.
5. Change the value data to 0.
6. Click OK and close the Registry Editor.
Conclusion
RAM compression is an important feature that can help to improve system performance by freeing up memory space. If you are experiencing slow performance and other issues in Windows 10, you can try forcing the system to compress memory more frequently using the methods outlined in this blog post. However, if you are still experiencing issues, you may need to upgrade your system’s memory or consider other hardware upgrades to improve performance.
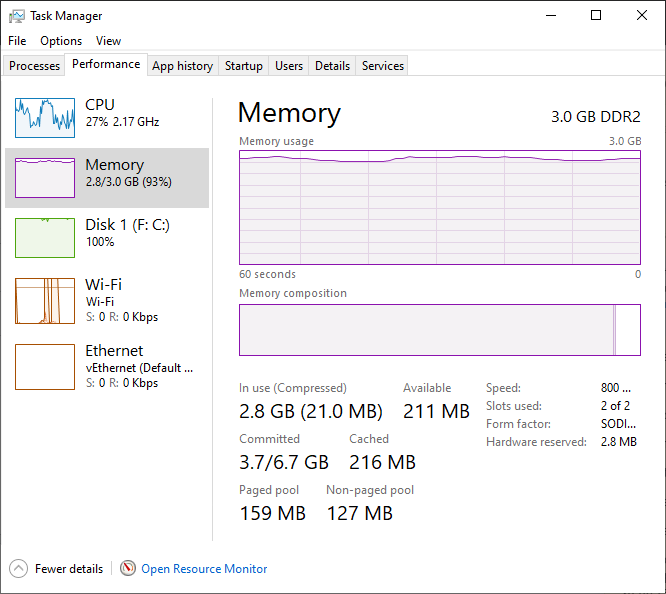
Memory compression cannot solve all problems related to insufficient RAM. Running Windows 10 on only 3GB of RAM is not practical because the Windows kernel consumes more memory than a BSD-based system like OSX, and applications on Windows tend to use more as well.
Additionally, the CPU performance may not be great because of the older DDR2 RAM, and the CPU cost of memory compression will be noticeable. Since Windows requires more disk access than OSX, having more RAM as a disk cache will be beneficial.
For a basic Windows 10 system, it’s recommended to have at least 4GB of RAM. However, if you use memory-intensive applications, it’s best to have at least 8GB of RAM, and RAM is relatively inexpensive (less than $4 per GB on eBay).
Alternatively, it may be worth considering retiring this over 10-year-old machine, as it was not designed to run Windows 10, and there may be other issues (such as GPU-related problems) as well.